Dependency properties is one concept which i always marvel. As programmer / developer i always like the concept, as by just introducing DP, so many stuff now is so easy(Read Template programming in XAML).
DP is called a BEAST (in Silverlight and WPF) for reasons of complexity involved in understanding them. Also, of course, because they are so powerful language paradigm. I sometimes do think DP did not actually got their due. I mean, so many efforts is gone into explaining Lambda expressions, LINQ, and other stuff but DP still remains a taboo.
So, when i took up to the task of explaining WPF, many were skeptical about my thought of actually introducing DP in second session itself. (the audiences had people from testing and not-so-much-into-coding). But i have always felt, new programming concept are like mathematics, once you have the concept, its interesting. But, mostly the concept part is ignored and then it all becomes a mystery.
here is a whirlwind introduction of DP… The ppts are here and the demo code here.
Below is explanations:
Purpose of dependency properties is to compute the value of a property based on values of other inputs available
DPs provide for
–Change Notification
–Callbacks
–Property value validation
–Property value inheritance *
–Participation in animations *
–Participation in Styles *
–Participation in Templates *
–Data binding
–Layout changes *
Overriding default data values *
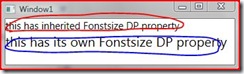
Example 1 – Explaining DP visual inheritance
consider:
1: <Window x:Class="Demo2.Window1"
2: xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
3: xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml" TextElement.FontSize="15"
4: Title="Window1" Height="300" Width="300">
5: <StackPanel>
6: <TextBlock Text="this has inherited Fonstsize DP property"></TextBlock>
7: <TextBlock Text="this has its own Fonstsize DP property" FontSize="20"></TextBlock>
8: </StackPanel>
9: </Window>
output is : The one encircled in Red inherits Font size from visual parent Window, which sets TextElement.FontSize to 15. The one encircled in Blue overrides this to font size 20.
Example2: Now lets implement our own version of DP inheritance for POC. The idea is to introduce a new DP “Text” for stackpanel which is propagated to its visual children DP.
Consider:
1: namespace Demo2
2: { 3: /// <summary>
4: /// Interaction logic for Window2.xaml
5: /// </summary>
6: public partial class Window2 : Window
7: { 8: public Window2()
9: { 10: InitializeComponent();
11: }
12: }
13: public class MyStackPanel : StackPanel
14: { 15:
16:
17: public string Text
18: { 19: get { return (string)GetValue(TextProperty); } 20: set { SetValue(TextProperty, value); } 21: }
22:
23: // Using a DependencyProperty as the backing store for Text. This enables animation, styling, binding, etc...
24: public static readonly DependencyProperty TextProperty =
25: DependencyProperty.Register("Text", typeof(string), typeof(MyStackPanel), 26: new FrameworkPropertyMetadata("stackPanel Default Text", 27: FrameworkPropertyMetadataOptions.Inherits));
28:
29: }
30:
31:
32: public class MyButton : Button
33: { 34: public string Text
35: { 36: get { return (string)GetValue(TextProperty); } 37: set { SetValue(TextProperty, value); } 38: }
39:
40: // Using a DependencyProperty as the backing store for Text. This enables animation, styling, binding, etc...
41: public static readonly DependencyProperty TextProperty =
42: MyStackPanel.TextProperty.AddOwner(typeof(MyButton),
43: new FrameworkPropertyMetadata("Button Default Text", FrameworkPropertyMetadataOptions.Inherits)); 44: }
45: }
We have added DP for both StackPanel and button. However in Button the DP is registered as
public static readonly DependencyProperty TextProperty =
MyStackPanel.TextProperty.AddOwner(typeof(MyButton),
new FrameworkPropertyMetadata("Button Default Text", FrameworkPropertyMetadataOptions.Inherits));
now here are scenarios:
1. if we set Text DP for both MyStackPanel and MyButton as below
1: <StackPanel>
2: <local:MyStackPanel x:Name="sp" Text="This is Test set by StackPanel">
3: <ContentPresenter Content="{Binding ElementName=sp, Path=Text}" ></ContentPresenter> 4: <local:MyButton Text="This is text set by MyButton"
5: Content="{Binding RelativeSource={x:Static RelativeSource.Self}, Path=Text}" 6: ></local:MyButton>
7: </local:MyStackPanel>
8: </StackPanel>
output is

2. if we set ONLY the Text in MYstackpanel, the MYButton Text will inherit from visual parent as below
1: <local:MyStackPanel x:Name="sp" Text="This is Test set by StackPanel">
2: <ContentPresenter Content="{Binding ElementName=sp, Path=Text}" ></ContentPresenter> 3: <local:MyButton
4: Content="{Binding RelativeSource={x:Static RelativeSource.Self}, Path=Text}" 5: ></local:MyButton>
6: </local:MyStackPanel>
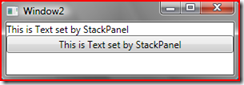 Notice button caption is same as Stackpanel
Notice button caption is same as Stackpanel
3. If we Do NOT set any text, the TEXT will assume default values for BOTH.
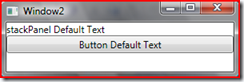
4. If we only set Button Text DP
1: <local:MyStackPanel x:Name="sp" >
2: <ContentPresenter Content="{Binding ElementName=sp, Path=Text}" ></ContentPresenter> 3: <local:MyButton Text="This is text set by MyButton"
4: Content="{Binding RelativeSource={x:Static RelativeSource.Self}, Path=Text}" 5: ></local:MyButton>
6: </local:MyStackPanel>

Notice in above case the Text DP is still default for stackpanel. that is DP is NOT propogated to visual parent from child.
We want to achieve the above case we have to make Attached DP property. I which parent property may be changed by the child element contained in parent
Attached DP Property
for this we will override an stackpanel and expose a Attached DP text which may be set by ANY visual children.
1: <StackPanel>
2: <local:MyStackAttached x:Name="sp">
3: <Button x:Name="btn" local:MyStackAttached.Text="This text set by child button" Content="OK"></Button>
4: </local:MyStackAttached>
5: <TextBox x:Name="textBox" ></TextBox>
6: </StackPanel>
1: namespace Demo2
2: { 3: /// <summary>
4: /// Interaction logic for Window3.xaml
5: /// </summary>
6: public partial class Window3 : Window
7: { 8: public Window3()
9: { 10: InitializeComponent();
11: // notice , we are getting DP value from btn and NOT stackpanel :D
12: textBox.Text = (string)btn.GetValue(MyStackAttached.TextProperty);
13: }
14: }
15:
16: public class MyStackAttached : StackPanel
17: { 18: static ContentPresenter contentPresenter = new ContentPresenter() { Height = 100.0, Width = 200.0 }; 19:
20: public MyStackAttached()
21: { 22: base.Children.Add(contentPresenter);
23: }
24:
25: public static string GetText(DependencyObject obj)
26: { 27: return (string)obj.GetValue(TextProperty);
28: }
29:
30: public static void SetText(DependencyObject obj, string value)
31: { 32: obj.SetValue(TextProperty, value);
33: }
34:
35: // Using a DependencyProperty as the backing store for Text. This enables animation, styling, binding, etc...
36: public static readonly DependencyProperty TextProperty =
37: DependencyProperty.RegisterAttached("Text", typeof(string), typeof(MyStackAttached), 38: new UIPropertyMetadata((o, e) =>
39: { 40: contentPresenter.Content = GetText(o);
41: }
42: ));
43: }
44: }
output:

Data Validation, Coerce using DP
The idea is to create a textbox which accepts only correct AGE values between 1 and 100. This is achieved by exposing a DP AGE.
1: public class MyTextBox : TextBox
2: { 3: public int Age
4: { 5: get { return (int)GetValue(AgeProperty); } 6: set { SetValue(AgeProperty, value); } 7: }
8:
9: // Using a DependencyProperty as the backing store for Age. This enables animation, styling, binding, etc...
10: public static readonly DependencyProperty AgeProperty =
11: DependencyProperty.Register("Age", typeof(int), typeof(MyTextBox), new FrameworkPropertyMetadata(1, 12: FrameworkPropertyMetadataOptions.None, new PropertyChangedCallback((o, e) => { }), new CoerceValueCallback((o, e) => 13: { 14: int current = (int)e;
15: if (current <=0 )
16: current = 1;
17: return current;
18: })),
19: new ValidateValueCallback((o) =>
20: { 21: int current = (int)o;
22: if (current > 100)
23: { return false; } 24: else
25: { return true; } 26: }));
27: }
the XAML looks like:
1: <StackPanel>
2: <TextBox x:Name="mytext"></TextBox>
3: <local:MyTextBox Age="{Binding ElementName=mytext, Path=Text, Mode=TwoWay}" 4: Text="{Binding RelativeSource={x:Static RelativeSource.Self}, Path=Age, Mode=TwoWay}" 5: ></local:MyTextBox>
6: </StackPanel>
Output:
 When Age value is <= 0 , the Age=1
When Age value is <= 0 , the Age=1
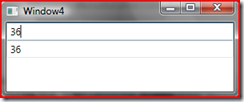 When age is valid
When age is valid
 when age > 100 then Age =1
when age > 100 then Age =1
Along with above i have also included a unit test case for the last scenario in the code.
Your thoughts / comments are welcome:
Technorati Tags:
XAML,
Silverlight,
WPF,
C#